The Cardiac Disease and Therapy laboratory blends advanced physiological assessment of cardiac function with leading molecular approaches for targeted, cell-specific manipulation of gene expression to understand how the heart adapts to stress in health and disease.
We have expertise in assessment of cardiac function in whole small animals (echocardiography), isolated hearts (systolic and diastolic, vascular function, ischaemic responses) and in characterisation of cell changes (enlargement, proliferation, death) in culture that allows advanced instrumentation and development of novel assessment techniques. This expertise is blended with targeted manipulation of protein expression in a time- and cell subtype-specificities manner through in vivo and in vitro gene editing, transfection and infection. We also characterise changes in cardiac biochemistry using immunocytochemistry, and RNA/DNA/protein quantification. Integrating this broad range of expertise to experiments enables us to undertake highly integrated assessment of the heart.
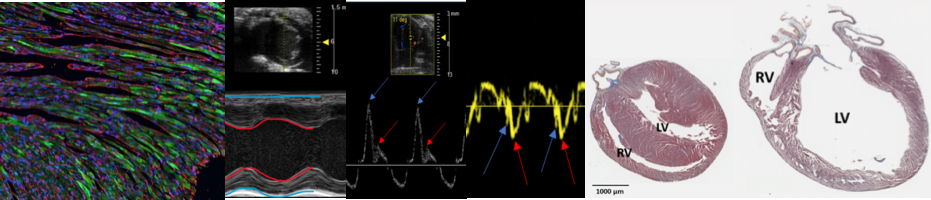
- Understanding how an old heart gets stiff
ARC Discovery Project DP200101152 - 2020-2022
CIA Reichelt, CIB Headrick, CIC Thomas, PI Patel
- How tissues generate the peptide hormone angiotensin II
ARC Discovery Project DP190102072, 2019-2021
CIA Thomas, CIB Reichelt
If you would like to make a tax deductible donation to Reichelt Cardiac Disease and Therapy, please contact med.advancement@uq.edu.au. Thank you for your support.

 Aging is accompanied by a stiffening of the heart and reduced function, which is accelerated by cardiovascular disease and leads to heart failure. How the heart stiffens is poorly understood. We have discovered a new mechanism involving structural membrane proteins (termed caveolae and cavins) and a signalling molecule (nitric oxide). The current research aims to use adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) to unravel the interplay between cardiac cells and these proteins/signals to cause stiffness and to determine whether this process governs normal aging of the heart. This work will advance understanding of how heart function is determined and reveal how the human heart changes with normal aging.
Aging is accompanied by a stiffening of the heart and reduced function, which is accelerated by cardiovascular disease and leads to heart failure. How the heart stiffens is poorly understood. We have discovered a new mechanism involving structural membrane proteins (termed caveolae and cavins) and a signalling molecule (nitric oxide). The current research aims to use adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) to unravel the interplay between cardiac cells and these proteins/signals to cause stiffness and to determine whether this process governs normal aging of the heart. This work will advance understanding of how heart function is determined and reveal how the human heart changes with normal aging.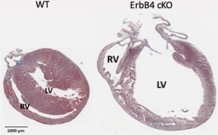
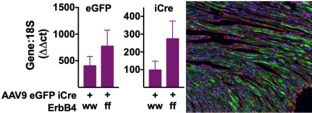
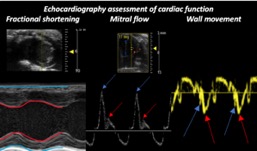 2. How does ErbB4 protect of hearts from Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)?
2. How does ErbB4 protect of hearts from Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction (HFpEF)?